Page 7 - AeM_April_2022
P. 7
RESEARCH, ANALYSIS & TRENDS
trade more than employment and economic growth.
Manufacturing in these countries has also started to
use more services rather than relying heavily on mak-
ing and selling their products.
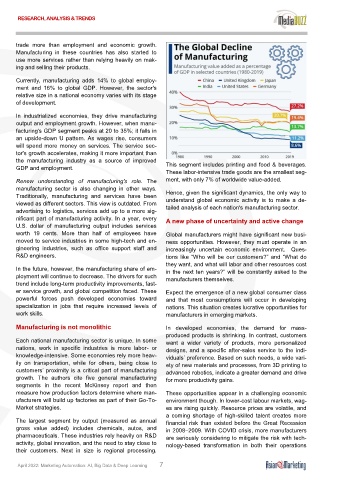
Currently, manufacturing adds 14% to global employ-
ment and 16% to global GDP. However, the sector's
relative size in a national economy varies with its stage
of development.
In industrialized economies, they drive manufacturing
output and employment growth. However, when manu-
facturing's GDP segment peaks at 20 to 35%; it falls in
an upside-down U pattern. As wages rise, consumers
will spend more money on services. The service sec-
tor's growth accelerates, making it more important than
the manufacturing industry as a source of improved
GDP and employment. This segment includes printing and food & beverages.
These labor-intensive trade goods are the smallest seg-
Renew understanding of manufacturing's role. The ment, with only 7% of worldwide value-added.
manufacturing sector is also changing in other ways.
Traditionally, manufacturing and services have been Hence, given the significant dynamics, the only way to
viewed as different sectors. This view is outdated. From understand global economic activity is to make a de-
advertising to logistics, services add up to a more sig- tailed analysis of each nation's manufacturing sector.
nificant part of manufacturing activity. In a year, every A new phase of uncertainty and active change
U.S. dollar of manufacturing output includes services
worth 19 cents. More than half of employees have Global manufacturers might have significant new busi-
moved to service industries in some high-tech and en- ness opportunities. However, they must operate in an
gineering industries, such as office support staff and increasingly uncertain economic environment. Ques-
R&D engineers. tions like “Who will be our customers?” and “What do
they want, and what will labor and other resources cost
In the future, however, the manufacturing share of em- in the next ten years?” will be constantly asked to the
ployment will continue to decrease. The drivers for such manufacturers themselves.
trend include long-term productivity improvements, fast-
er service growth, and global competition faced. These Expect the emergence of a new global consumer class
powerful forces push developed economies toward and that most consumptions will occur in developing
specialization in jobs that require increased levels of nations. This situation creates lucrative opportunities for
work skills. manufacturers in emerging markets.
Manufacturing is not monolithic In developed economies, the demand for mass-
produced products is shrinking. In contrast, customers
Each national manufacturing sector is unique. In some want a wider variety of products, more personalized
nations, work in specific industries is more labor- or designs, and a specific after-sales service to the indi-
knowledge-intensive. Some economies rely more heav- viduals’ preference. Based on such needs, a wide vari-
ily on transportation, while for others, being close to ety of new materials and processes, from 3D printing to
customers’ proximity is a critical part of manufacturing advanced robotics, indicate a greater demand and drive
growth. The authors cite five general manufacturing for more productivity gains.
segments in the recent McKinsey report and then
measure how production factors determine where man- These opportunities appear in a challenging economic
ufacturers will build up factories as part of their Go-To- environment though. In lower-cost labour markets, wag-
Market strategies. es are rising quickly. Resource prices are volatile, and
a coming shortage of high-skilled talent creates more
The largest segment by output (measured as annual financial risk than existed before the Great Recession
gross value added) includes chemicals, autos, and in 2008–2009. With COVID crisis, more manufacturers
pharmaceuticals. These industries rely heavily on R&D are seriously considering to mitigate the risk with tech-
activity, global innovation, and the need to stay close to nology-based transformation in both their operations
their customers. Next in size is regional processing.
April 2022: Marketing Automation: AI, Big Data & Deep Learning 7